FromDual TechFeed (en)
Typical automated MySQL maintenance jobs
[http://www.blogger.com/profile/11195863756524022642 Shinguz] said…
Hi knetknight
Thanks for your comment.
When your are facing time/scheduling issues I recommend you to go through the MySQL online documentation (Chapter: Table Maintenance Statements and Restrictions on InnoDB Tables) because some of these commands have no effect on some table types (InnoDB) and some of them do the work already done in a previous command.
Regards Oli
Taxonomy upgrade extras:
MySQL Cluster: No more room in index file
[http://www.blogger.com/profile/11195863756524022642 Shinguz] said… Hi Matthew
Thanks for your comment. This could have helped a lot. I do NOT ask why there was no message like:
Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.10 sec)
or why the real cause was not displayed at all…
Taxonomy upgrade extras:
MySQL Cluster: No more room in index file
Recently we were migrating an InnoDB/MyISAM schema to NDB. I was too lazy to calculate all the needed MySQL Cluster parameters (for example with ndb_size.pl) and just took my default config.ini template.
Because I am really lazy I have a little script doing this for me (alter_engine.pl).
But suddenly my euphoria was stopped abruptly by the following error:
MySQL error code 136: No more room in index file
The usual command that helps me in such a situation is a follows:
# perror 136
MySQL error code 136: No …Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Cluster Index File
Possible memory leak in NDB-API applications?
A customer has recently experienced a possible memory leak in its NDB-API application. What he did was something like:
# ps aux | grep <pid>
over time and then he saw the RSS increasing. When he would have had a look a little longer he would have seen that the RSS consumption would increase up to a certain level and then becomes stable. Which is the expected behavior.
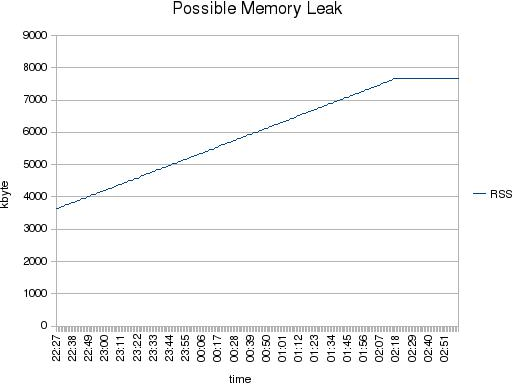
But how to explain to the customer that his application, which was in fact not doing anything, consumes more RSS?
With a diff over …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Memory Leak Ndb-Api Memory
Active/active failover cluster with MySQL Replication
Electing a slave as new master and aligning the other slaves to the new master
In a simple MySQL Replication set-up you have high-availability (HA) on the read side (r). But for the master which covers all the writes (w) and the time critical read (rt) there is no HA implemented. For some situations this can be OK. For example if you have rarely writes or if you can wait until a new Master is set up.
But in other cases you need a fast failover to a new master.
In the following article it is shown how to …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English High Availability Mysql Replication Cluster Active-Active Failover
Typical automated MySQL maintenance jobs, query cache
The following maintenance jobs are typically run against a MySQL database:
- Backup
- Clean-up binary logs
- Optimize tables
- Purge query cache
- Rotate binary logs
Backup
A backup is not a typical maintenance job. But it behaves more or less like one. The backup should be done regularly depending on the restore/PITR (Point in Time Recovery) requirements.
Make sure, that in the backup all the necessary files (data files, transaction log files, configuration files and binary log files) are included. To prove that …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Operations Mysql Mainenance Jobs Query Cache
My thoughts about MySQL (Cluster) replication
According to Johans wishes I write down my concerns about MySQL (Cluster) replication. These items are things I run again and again into it with customers:
- SQL-nodes are still loosing too easy connection to cluster after data node or management node restart (which leads into gaps, see next point). Automatic failover or reconnection is just a dream (maybe it works in about 90% of the cases at least).
- Gaps: Whenever I do a cluster reconfiguration (should not be necessary too often, see loosing connection …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Replication Mysql Cluster
Some more details about DiskSyncSize
The parameter DiskSyncSize is a MySQL Cluster parameter and was added in MySQL 5.1.23.
After the amount of stored bytes of data per file, the data node will fsync (flush) the LCP file to disk, even if a fsync is not needed for consistency.
This is done because the OS will otherwise buffer all the writes, and when a fsync is really needed, it can take a lot of time…
Originally this parameter was hard coded. Now it defaults to 4 Mbyte.
The parameter DiskSyncSize is related to the parameters …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Cluster Disksyncsize Parameter
With MySQL-Enterprise Montior through firewalls
Sometimes it is nice to show customers the functionality of MySQL-Enterprise Monitor (aka Merlin). I install the agents on the servers and the dashboard runs on my laptop. But very often only ssh is open to these servers.
So how to dig a whole through the firewall for MySQL-Enterprise Monitor?
# ssh -R 18080:localhost:18080 oli@where_the_agent_sits
Maybe trivial for you but for me its hard to remember…
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Enterprise Monitor Firewall
Sparse files
What is a sparse file?
“A sparse file is a file where space has been allocated but not actually filled with data. These space is not written to the file system. Instead, brief information about these empty regions is stored, which takes up much less disk space. These regions are only written to disk at their actual size when data is written to them. The file system transparently converts reads from empty sections into blocks filled with zero bytes at runtime.”
[ 1
]
In other words: Files are not …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Sparse Files
Ranking in MySQL results
A friend of me asked me long time ago: “How can I have a ranking on a result with MySQL?”. Now I found some time to write it down:
Lets do first some preparation for the example:
CREATE TABLE sales (
id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, fruit VARCHAR(32)
, amount DECIMAL
);
INSERT INTO sales
VALUES (NULL, 'apple', 12.75), (NULL, 'orange', 1.89), (NULL, 'pear', 19.23)
, (NULL, 'banana', 4.25), (NULL, 'cherry', 123.75), (NULL, 'plum', 23.15)
;
Now lets query:
SELECT …Taxonomy upgrade extras: Mysql Ranking Result
MySQL logon trigger
With MySQL 5.0 the database provides trigger functionality on INSERT, REPLACE, UPDATE and DELETE.
Those of you who know some other RDBMS know, that there are also some system events where one would like to have triggers.
Unfortunately MySQL does not (yet) provide such functionality. This is sad because as database administrator this would be sometimes very helpful.
But you can build your own LOGON and STARTUP trigger.
MySQL provides some hooks for these events…
Complete Story (PDF 160 kbyte).
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Logon Trigger Trigger Login Trigger Audit
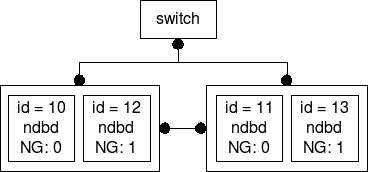
MySQL Cluster restore
Recently the question came up if it is faster to restore a MySQL cluster when all nodes are up or only ONE node from each node group during restore.
The answer from our gurus was: All nodes up during restore! I wanted to find out why. So I set up the following cluster and started to measure:
MySQL Cluster set up
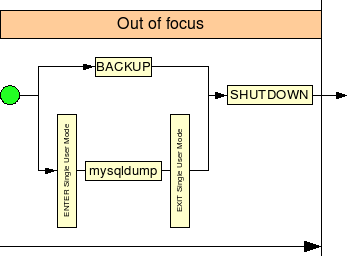
MySQL Cluster backup
The backup is not that interesting. But I made the drawing for possible future use :-) :
MySQL Cluster restore
For the restore there are 4 different ways thinkable:
- Restore …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Backup Restore Recovery Mysql Cluster
MyEnv (MySQL and MariaDB BasEnv)
What is MyEnv?
MyEnv is a tool to run several MySQL or MariaDB database instances on ONE host. You can even run multiple database instances with different binary versions. We call this multi-instance set-ups.
With MyEnv a multi-instance set-up is more comfortable to handle than with mysqld_multi (old) or Systemd services (new) and it provides more useful functionality.
Using MyEnv does not need the use of the root user to operate MySQL and MariaDB database instances. Thus it is appropriate for classical …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: Environment Virtualization Consolidation Multi Instance Saas Myenv License Container Docker
MySQL Active - Active Clustering
It is possible to use an active - active shared-disk cluster in MySQL in some cases. For doing this you have to fulfill the following requirements:
- Works with MyISAM tables only.
- POSIX-locking compliant cluster file system on the device (such as OCFS2 or GFS).
- External locking must be enabled.
- The MySQL query cache must be turned off.
- The MySQL delay key write must be turned off.
- OS where file locking is supported in MySQL.
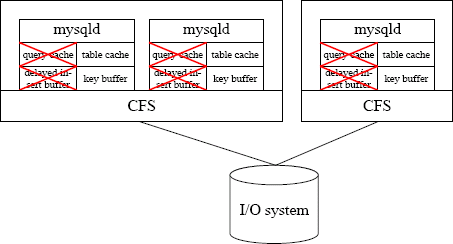
Interested? To read more, follow the link: MySQL active - active Cluster (PDF 157 …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Performance Active-Active Clustering Cluster
Transaction performance
Transaction performance relates among other things from I/O performance. This means hard disk performance.
Hard disk performance
When you select a hard disk, an important feature to consider is the performance (speed) of the drive. Hard disks come in a wide range of performance capabilities. As is true of many things, one of the best indicators of a drive’s relative performance is its price. An old saying from the automobile-racing industry is appropriate here: “Speed costs money. How fast do you want …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Performance Tuning Performance Transaction
Round-Robin Database Storage Engine (RRD)
In a round-robin database (RRD) usually time-series data like network bandwidth, temperatures, CPU load etc. is stored. The data is stored in the way that system storage footprint remains constant over time. This avoids resource expensive purge jobs and reduces complexity.
MySQL does NOT yet provide this kind of storage engine. Although some people were thinking about and some prototypes exists.
Nevertheless in this paper it is shown how you can build your own RRD tables: Round-Robin Database Storage …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Storage Engine Rrd Round-Robin Database
SATA Flash Solid State Disk up to 160 Gbyte announced!
The price for a 160 Gbyte disk will be around USD 15'000. This is still a bit expensive. But the access time is around 0.5 ms (both for reading and writing) which is around 10 times faster than a normal 15'000 rpm SCSI disk! The disk has NO cache because it is a cache itself (according to the supplier. Maybe this will change in the future). And the lifetime of a cell is > 5 mio writes. For the same performance one needs usually an array of around 10 disks. If your database is heavily write-I/O bound you …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Performance Sata Flash Solid State Disk
MySQL Multi-Master - Single-Slave - Replication
MySQL provides its replication for High Availability (HA) and for read Scale-out. Generally it is known that in a MySQL replication you can only replicate from one Master to many slaves. In this paper it is shown how a set-up can look like to replicate from two masters to one slave.
Caution: Handle this information with care!!!
Taxonomy upgrade extras: Multi-Master Slave Replication Multi-Source
Profiling MySQL with oprofile
Probably the answer to this question is already known. But we want to prove it and by the way learn to deal with MySQL and oprofile.
Taxonomy upgrade extras: English Mysql Profiling Oprofile

