Feed Aggregator
Operating System Signals on different platforms
shell> kill -l
Linux
| 1) SIGHUP | 2) SIGINT | 3) SIGQUIT | 4) SIGILL |
| 5) SIGTRAP | 6) SIGABRT | 7) SIGBUS | 8) SIGFPE |
| 9) SIGKILL | 10) SIGUSR1 | 11) SIGSEGV | 12) SIGUSR2 |
| 13) SIGPIPE | 14) SIGALRM | 15) SIGTERM | 16) SIGSTKFLT |
| 17) SIGCHLD | 18) SIGCONT | 19) SIGSTOP | 20) SIGTSTP |
| 21) SIGTTIN | 22) SIGTTOU | 23) SIGURG | 24) SIGXCPU |
| 25) SIGXFSZ | 26) SIGVTALRM | 27) SIGPROF | 28) SIGWINCH |
| 29) SIGIO | 30) SIGPWR | 31) SIGSYS | |
| 34) SIGRTMIN | 35) SIGRTMIN+1 | 36) SIGRTMIN+2 | |
| 37) SIGRTMIN+3 | 38) SIGRTMIN+4 | 39) SIGRTMIN+5 | 40) SIGRTMIN+6 |
| 41) SIGRTMIN+7 | 42) SIGRTMIN+8 | 43) SIGRTMIN+9 | 44) SIGRTMIN+10 |
| 45) SIGRTMIN+11 | 46) SIGRTMIN+12 | 47) SIGRTMIN+13 | 48) SIGRTMIN+14 |
| 49) SIGRTMIN+15 | 50) SIGRTMAX-14 | 51) SIGRTMAX-13 | 52) SIGRTMAX-12 |
| 53) SIGRTMAX-11 | 54) SIGRTMAX-10 | 55) SIGRTMAX-9 | 56) SIGRTMAX-8 |
| 57) SIGRTMAX-7 | 58) SIGRTMAX-6 | 59) SIGRTMAX-5 | 60) SIGRTMAX-4 |
| 61) SIGRTMAX-3 | 62) SIGRTMAX-2 | 63) SIGRTMAX-1 | 64) SIGRTMAX |
Solaris 10 (x86, Sparc)
| 1) SIGHUP | 2) SIGINT | 3) SIGQUIT | 4) SIGILL |
| 5) SIGTRAP | 6) SIGABRT | 7) SIGEMT | 8) SIGFPE … |
Taxonomy upgrade extras: operating system, signal, platform, kill,
Quick links to the MySQL documentation
MySQL Statement Syntax
Data Definition Language (DDL) Statements
Data Manipulation Language (DML) Statements
| CALL | DELETE | DO | HANDLER |
| INSERT | LOAD DATA INFILE | REPLACE | SELECT |
| TRUNCATE TABLE | UPDATE |
MySQL Utility Statements
| DESCRIBE | EXPLAIN | HELP | USE |
MySQL Transactional and Locking Statements
| START TRANSACTION | COMMIT | ROLLBACK | SAVEPOINT |
| ROLLBACK TO SAVEPOINT | LOCK TABLES | UNLOCK TABLES | SET TRANSACTION |
| XA Transactions |
Account Management Statements
| CREATE USER | DROP USER … |
Taxonomy upgrade extras: documentation, general query log,
MySQL Cluster overview
This is a chaotic collection of my MySQL Cluster experience…
Table of Contents
- config.ini template
- my.cnf template
- General Rules and/or experience
- MySQL Cluster restore
- Skript for converting tables to NDB (alter_engine.pl)
- MySQL Cluster memory sizing
config.ini template
A generic MySQL Cluster configuration file (config.ini) to start with. It is pretty much what the MySQL Cluster experts recommend right now:
#
# config.ini
#
# This configuration file is fore MySQL Clusters 6.2 and above...
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
[TCP DEFAULT]
# Default is too small!
SendBufferMemory = 2M
ReceiveBufferMemory = 2M
# When this is configured together with section above ndb_mgmd will
# return with erro -1 (255). This is a bug and should be fixed earlier
# or later!
# When you move this section to the bottom it should work.
# You need one TCP section for EACH cluster node pair!
# (for example: 4 nodes = 6 sections)
# [TCP]
#
# NodeId1: 10
# …Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql cluster,
MySQL Cluster memory sizing
MySQL Cluster is pretty fast. The reason for this is, that it is completely memory based. Nowadays memory is still, in contrary to disk, limited to your systems. Thus, before installing a MySQL Cluster you have to calculate the amount of memory you need.
To say it in advance: You should consider to only use 64-bit Linux system with huge amount (4 - 64 GB) of RAM!
In release 5.1 MySQL Cluster became disk based. Now you have the possibility to swap out some data to disk. How much it is we will probably see a little further down…
Calculating or estimating
For calculating or estimating how much Memory you need, you have several different possibilities:
- You can do it by hand.
- This OO calc spread sheet helps you.
- You can have it much easier by using ndb_size.pl (or the newer not yet official released version → link).
- Or you can extrapolate from a consisting data set.
Memory usage
First we want to see where memory is used in Cluster. When we do a ps we know how much memory our cluster process allocates:
# …Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql cluster, memory, sizing,
MySQL hints
Table of Contents
- Result set with temporary sequence
- Determination of optimal length of prefixed indexes
- Using MySQL keywords in table or columm names
- Missing Primary Key Index
- Problems while installing a MySQL 5.5 database
- InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT at 2nd position
Result set with temporary sequence
Sometimes you would like to have a result set with something like a rownum. You can do this at least in the following two ways:
a) with a TEMPORARY MEMORY table:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE mem (
seq INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, data VARCHAR(32)
) ENGINE=MEMORY;
INSERT INTO mem
SELECT NULL, data
FROM test
LIMIT 5;
SELECT *
FROM mem;
+-----+------+
| seq | data |
+-----+------+
| 1 | abc |
| 2 | def |
| 3 | ghi |
| 4 | abc |
| 5 | def |
+-----+------+
b) with a user defined variable
SET @seq=0;
SELECT @seq:=@seq+1, data FROM test WHERE id < 100 LIMIT 5;
+--------------+------+
| @seq:=@seq+1 | data |
+--------------+------+
| 1 | abc |
| 2 | def |
| …Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, migration, innodb, hint, primary key, index, prefixed index, sequence, temporary, keyword, auto_increment, memory table,
DBA wisdoms
Controlling developers is like herding cats.
Kevin Loney, Oracle DBA Handbook
Oh no, it’s not. It’s much harder than that!
Bruce Pihlamae, long-term Oracle DBA
Do not assume!
Unknown IT specialist
Backups ist was für Warmduscher!
(engl. Backup is for sissies!)
Unkown DBA
Yesterday (the DBA version)
Yesterday,
All those backups seemed a waste of pay.
Now my database has gone away.
Oh I believe in yesterday.
Suddenly,
There’s not half the files there used to be,
And there’s a milestone hanging over me
The system crashed so suddenly.
I pushed something wrong
What it was I could not say.
Now all my data’s gone
and I long for yesterday-ay-ay-ay.
Yesterday,
The need for back-ups seemed so far away.
I knew my data was all here to stay
Now I believe in yesterday.
The SISO DB principle: Shit In - Shit Out
Der altehrwürdigste aller Tuning Ansätze: Change the statement!
(engl. The most time-honoured approach of tuning: Change the statement!)
Robert Staudach?
There is no …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: backup, dba, tuning, database administrator,
MySQL trouble shooting
Table of Contents
max_open_fileswarning duringmysqldstartup- Troubles after NON recommended upgrade path
Com_*counters not updated inSHOW STATUSERROR 1300 (HY000): Invalid utf8 character string- MySQL crashes during import
- MySQL workbench gives an openGL error
max_open_files warning during mysqld startup
Problem
[Warning] Changed limits: max_open_files: 1024 max_connections: 100 table_cache: 457
[Warning] Could not increase number of max_open_files to more than 1024 (request: 1070)
Explanation
The operating system hard limit of open files was exceeded.
Analysis
Finding the soft and hard limits of open files for your account you can find like this:
# ulimit -Sa | grep "open files"
open files (-n) 1200
# ulimit -Ha | grep "open files"
open files (-n) 8192
This corresponds to:
mysql> show variables like ...
+-------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------+-------+
| open_files_limit | 1200 |
| table_cache …Taxonomy upgrade extras: trouble shooting, open_files_limit, table_open_cache, limitnofile,
MySQL Questions & Answers
Table of Contents
- Search with special characters
- Why is InnoDB disabled?
- How to find MySQL system information?
- What is the difference between MySQL certified server and community server?
- MySQL monitoring
- MySQL backup
- Corrupt MyISAM table
- How to compile MySQL
- Test restore procedure
- Reset a MySQL user password
- Reset the MySQL root user password
- How to enable the InnoDB plugin
- Storage Engines shipped with MariaDB / MySQL
- Compiling MySQL Cluster ndb-test fails
- NDB information schema does not show up
- Hyper Threading (HT) enabled?
- How to make a patch for MariaDB?
- Where does the InnoDB AUTO-INC waiting come from?
- My character encoding seems to be wrong. How can I fix it?
- I think my Slave is not consistent to its Master any more. How can I check this?
- My MySQL Server is swapping from time to time. This gives hick-ups in MySQL. How can I avoid this?
- How can I find which I/O scheduler my device is using?
- How can I find why my mail is not sent?
Search with special characters
This Question has been moved to the Forum. …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: backup, restore, recovery, mysql cluster, innodb, monitoring, lvm, myisam, snapshot, compiling, swap,
Limitations of MySQL
Often asked but informations are spread around: The limitations of MySQL.
If you know any other MySQL limitations, please let us know.
Table of Contents
- General limitations of MySQL
- Limitations of MySQL 4.1
- Limitations of Joins
- Limitations of the MyISAM storage engine
- Limitations of MySQL 5.0
- Limitations of Joins
- Limitations of the MyISAM storage engine
- Limitations of InnoDB
- Limitations of MySQL 5.1
- Limitations of Joins
- Limitations of Partitions
- Limitations of MySQL Cluster
- Limitations in Galera Cluster for MySQL
General limitations of MySQL
32-bit binaries cannot address more than 4 Gbyte of memory. This is not a MySQL limitation, this is a technical limitation.
BLOB’s are limited to 1 Gbyte in size even thought you use LONGBLOB because of a limitation in the MySQL protocol: The protocol limit for max_allowed_packet is 1GB.
Limitations of MySQL 4.1
Limitations of Joins
In MySQL 4.1, the maximum number of tables that can be referenced in a single join is 61. This also applies to the number …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, mysql cluster, limitation, limitations, galera, general query log,
MySQL User Defined Function (UDF) collection
I really like this new toy called UDF. So I try to provide some more, hopefully useful, functionality.
A list of what I have done up to now you can find here:
- Query and change InnoDB spin_wait_delay: udf_spin_wait_delay.tgz
- Send message to the MySQL error log: udf_log_error.tgz, works also with MySQL 5.1.42
If you have some more suggestions, please let me know. If you need some special features as UDF talk to our consulting services if they can implement it.
Get and set InnoDB spin_wait_delay
mysql> CREATE FUNCTION spin_wait_delay
RETURNS INTEGER SONAME "udf_spin_wait_delay-5.1.30-linux-i686-glibc23.so";
mysql> SELECT spin_wait_delay();
+--------------------+
| spin_wait_delay(5) |
+--------------------+
| 5 |
+--------------------+
mysql> SELECT spin_wait_delay(8);
+--------------------+
| spin_wait_delay(8) |
+--------------------+
| 8 |
+--------------------+
mysql> DROP FUNCTION spin_wait_delay;
Send message to MySQL error log
mysql> …Taxonomy upgrade extras: udf, user-defined function,
The handler_read_* status variables
Because I do a lot of Performance Tuning gigs I get often in contact with these status variables. In the beginning I had a problem to understand them and now I have a problem to memorize the relation of the name and the meaning. Therefore I wrote this little summary:
Prepare the example
To show you the effect I have worked out a little example:
CREATE TABLE test (
id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, data VARCHAR(32)
, ts TIMESTAMP
, INDEX (data)
);
INSERT INTO test
VALUES (NULL, 'abc', NOW()), (NULL, 'abc', NOW()), (NULL, 'abd', NOW())
, (NULL, 'acd', NOW()), (NULL, 'def', NOW()), (NULL, 'pqr', NOW())
, (NULL, 'stu', NOW()), (NULL, 'vwx', NOW()), (NULL, 'yza', NOW())
, (NULL, 'def', NOW())
;
SELECT * FROM test;
+----+------+---------------------+
| id | data | ts |
+----+------+---------------------+
| 1 | abc | 2008-01-18 16:28:40 |
| 2 | abc | 2008-01-18 16:28:40 |
| 3 | abd | 2008-01-18 16:28:40 |
| 4 | acd | 2008-01-18 16:28:40 | …Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, handler, handler interface, status variables, status,
Performance Tuning Key for MySQL
This MySQL Performance Tuning Key should give you a guide how to best tune you MySQL database systematically… It should also work similar for other RDBMS.
Also check our MySQL Performance Monitor
For a database configuration tuning only please look first at our MySQL database health check.
If this MySQL Database Health Check does NOT solve your problem our specialized Performance Tuning and Architecture Consultants can help you for sure!
Caution: Some recommendations are dangerous! Dangerous means you can loose or get inconsistent data in certain cases. Only use them if you know what you are doing!!!
Acknowledgement
Thanks to the following people for hints:
- Jens Bollmann
Efficiency of Performance Tuning measurements
Before you start tuning you should think about the following graph:
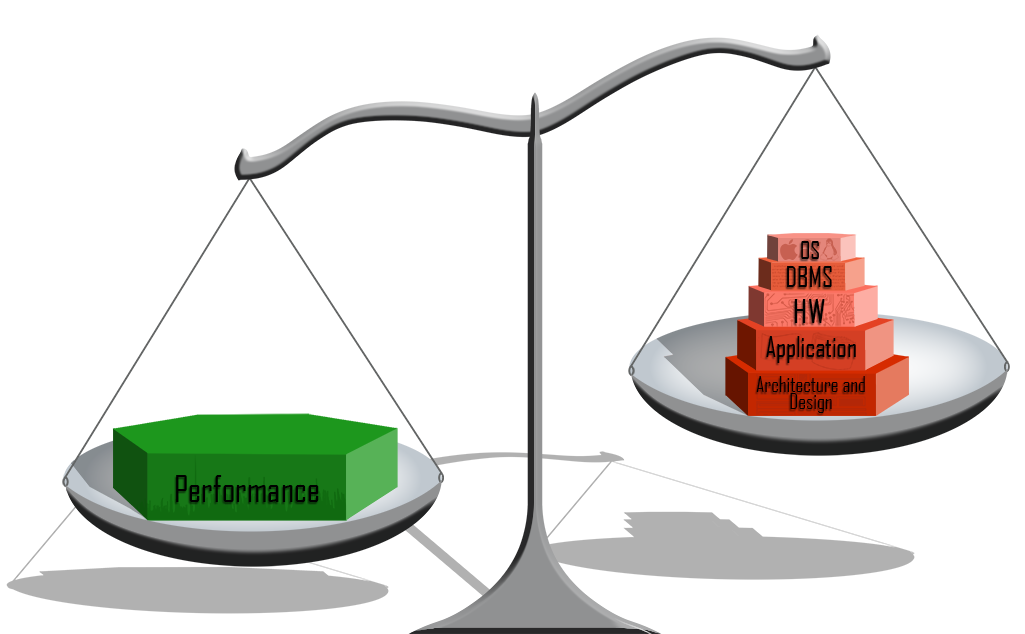
And see also Relative Impact on Performance (p. 33 ff.)
Start
(last updated 2010-10-03)
000. Do you have performance problems?
001. Have you ever …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, performance, tuning,
Hunting the core
Core files under Linux
When dealing with MySQL crashes it is very useful to get the core files for further debugging. I have collected all the informations I found about it and wrote it together here:
Find core files
# find $HOME -name "core*"
/home/oli/core.6440
# file core
core: ELF 32-bit LSB core file Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), SVR4-style
See who caused the core file:
# strings core.6440 | head
CORE
CORE
mysqld
/home/mysql/product/mysql-5.1.30/bin/mysqld --defaults-file=/home/mysql/product
...
Soft and hard limit of core files size
(in blocks of 512 byte?→seems to be 1k blocks!)
# ulimit -Sc
# ulimit -Hc
# ulimit -c unlimited
Getting an setting core file pattern
# cat /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
core
# cat /proc/sys/kernel/core_uses_pid
0
# echo "1" > /proc/sys/kernel/core_uses_pid
# echo "/tmp/corefiles/core" > /proc/sys/kernel/core_pattern
Provoke a core dump
# kill -s SIGSEGV $$
or
# kill -11 <pid>
Dump more information
# cat …Taxonomy upgrade extras: debug, trace, core,
Reading other processes memory
As you probably have experienced yet MySQL does not always provide all internal information as you might want to have them and as you are used to have from other RDBMS.
MySQL plans to improve this implementing the/a performance schema and its probably already partly done in MySQL 5.4. But who knows when this will be finished and what it contains at all…
What is not provided to me I want to gather myself… But how? Other RDBMS provide interfaces to attach applications directly to their memory to retrieve information. But MySQL does not. So I was looking for a way to read an other process memory.
I have no clue about programming and thus changing MySQL code was out of focus. Further I am looking for a solution you can use immediately on a running systems at consulting gigs. Some tries to read /proc/
<pid
>/mem with a little php script failed.
An article by Domas M. helped me. I do not have to write something myself I can use a tool already existing to do the work. But gdb is not installed on …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: process, memory, debug, trace,
MySQL Monitoring solutions
Basic solutions (CLI)
Those solutions are run from the command line (CLI):
- top (man)
- vmstat (man)
- iostat (man), mpstat (man), pidstat in package sysstat
- mytop, a Mytop Introduction
- dstat
- free (man)
- procinfo (man)
- mpstat (man)
- mTop
- InnoTop
Advanced solutions
More advanced MySQL database and host monitoring solutions with graphs and/or history and/or hints are:
| MySQL Performance Monitor | The FromDual Performance Monitor for MySQL/MariaDB is a monitoring solution based on Zabbix. It is freely available. More information about it you can find here. |
| MySQL Enterprise Monitor | The MySQL Enterprise Monitor (aka Merlin or MEM) serves as an automated assistant for MySQL database administrators. For MySQL customers only! |
| cmon | CMON - the Cluster Monitor for MySQL Cluster. CMON is the most comprehensive monitor for MySQL Cluster and collect all information that is possible to collect from the data nodes and management servers. |
| MySQL Activity Report | The MySQL Activity Report package is a tool to help MySQL … |
Taxonomy upgrade extras: performance tuning, mysql, monitoring, performance monitoring, mytop, innotop,
FromDual sitemap
Performance Tuning, Benchmarking, Capacity Planning and Monitoring
MySQL Database Health Check for MySQL/MariaDB
Wie der MySQL Optimizer schummelt, wenn es um MySQL Cluster geht…
How the MySQL Optimizer with MySQL Cluster is cheating you…
My thoughts about MySQL (Cluster) replication
My wish for the New Year: MySQL DBA’s, please install iostat on your servers!
Backup/Restore/Recovery, Operations and Consulting
What’s going on when MySQL does operations on partitions?
FromDual consulting tool collection
MySQL Configuration File sample (my.cnf/my.ini)
MyEnv for Multi-Database set-ups
Logging users to the MySQL error log
Architecture, Design and High Availability
Stealthy migrating MySQL tables and MySQL data access interfaces using enlarged …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: document, article, summary, overview, content,
Profiling MySQL with oprofile
Why is is data load with LOAD DATA INFILE so much faster?
Probably the answer to this question is already known. But we want to prove it and by the way learn to deal with oprofile.
For the test MySQL 5.0.28 was used and 100k rows were loaded into a table sales which looks as follows:
CREATE TABLE sales (
sales_id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, product_name VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL
, product_price DECIMAL(8,2) NOT NULL
, product_amount SMALLINT NOT NULL
) ENGINE = MyISAM;
The following load times were messured:
| Test | MyISAM | InnoDB | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOAD DATA INFILE | 0.85 s | 2.51 s | |
| Multi row INSERT | 2.69 s | 4.48 s | |
| Single row INSERT | 15.0 s | 881 s | [ 1 ] |
| Single row INSERT w/o LOCK TABLE | 15.1 s | 18.1 s | [ 2 ] |
But now we want to know what happens into mysqld during this load. For measuring this see also:
opcontrol --init
opcontrol --setup --separate=lib,kernel,thread --no-vmlinux
opcontrol --start-daemon
ps axuwww| grep opro
opcontrol --start
do the …Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, profiling, oprofile, profile,
Materialized Views with MySQL
Table of Contents
- What is a Materialized View?
- Implement your own Materialized Views
- Refreshing materialized views
- Hands on
- Create your own Materialized View:
- Refresh Materialized View on demand
- Refresh Materialized View immediate
- Materialized Views with snapshotting functionality
- Some performance benchmarks for our Materialized Views:
- Outlook
- Conclusion
- Literature
What is a Materialized View?
A Materialized View (MV) is the pre-calculated (materialized) result of a query. Unlike a simple VIEW the result of a Materialized View is stored somewhere, generally in a table. Materialized Views are used when immediate response is needed and the query where the Materialized View bases on would take to long to produce a result. Materialized Views have to be refreshed once in a while. It depends on the requirements how often a Materialized View is refreshed and how actual its content is. Basically a Materialized View can be refreshed immediately or deferred, it can be refreshed fully or to a certain point in time. …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: mysql, trigger, materialized views, materialised views, sql/psm,
MySQL Federated Storage Engine
What is a Federated Table?
A Federated Table is a table which points to a table in an other MySQL database instance (mostly on an other server). It can be seen as a view to this remote database table. Other RDBMS have similar concepts for example database links.
What can I do with a Federated Table?
To show what you can do with a federated table let us assume the following constellation: Two MySQL databases on two different servers. The first one called provider (it provides the data) the second one called requester (it requests the data). For a better understanding see the following example:
CREATE TABLE provider (
a INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
, b VARCHAR(32) NULL
, INDEX b_i (b)
) ENGINE = MyISAM;
INSERT INTO provider
VALUES (NULL, 'Apfel'), (NULL, 'Birne'), (NULL, 'Pflaume')
, (NULL, 'Banane'), (NULL, 'Kirsche'), (NULL, 'Quitte');
SELECT * FROM provider;
CREATE TABLE requester (
a INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL …Taxonomy upgrade extras: storage engine, federated tables, general query log,
FromDual consulting tool collection
The following tools we use sometimes for our consulting engagements…
Caution: These tools are NOT for production use! Use with care!
Tools
- allocate.c
- backslashG2table.pl
- general2bench.pl
- memuse.pl
- memwaster.c
- MySQLprofiler
- pointer_size.c
- alter_engine.pl
- commit_demo.pl
- test.sh
- vm_mon.sh
- read_process_memory.c
- read_process_memory.sh
- cluster_initial_test.pl
- mem_map.pl
- csv_converter.pl
- mem_tracker.sh
- filesystem_table.php
Sample Databases
- MySQL world: world.tgz (92 kbyte, runs with version 4.1 (tested on 4.1.16))
- Oracle’s scott/tiger for MySQL: scott_tiger.tgz (1.2 kbyte, runs with version 4.1 (tested on 4.1.16))
- Mondrian’s FoodMart: FoodMart.tar.bz2 (2.9 Mbyte, runs with version 5.0 (tested on 5.0.18)) or the adapted FoodMart which seems also to work with 5.1.16 and even MySQL Cluster!
- FoodMart-2.tar.gz (13 Mbyte). Tested with MySQL 5.5, with much more data, newer date ranges and some other improvements…
allocate.c
Very evil memory reclaimer, tries to allocate specified amount of …
Taxonomy upgrade extras: tool, consulting, memory, san, general query log,

